A mirage is a natural optical phenomenon that causes the appearance of a body of water or an object on a hot day. It is caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. Mirages are often seen on highways, deserts, and other hot, flat surfaces.
Mirages can be a beautiful and fascinating sight, but they can also be dangerous. Drivers who see a mirage of water on the road may be tempted to drive into it, which could lead to a crash. Mirages can also cause ships to sail off course and planes to crash.
The study of mirages has a long history. In the 10th century, the Arab mathematician Ibn al-Haytham wrote a book about mirages in which he explained how they are caused by the bending of light. In the 17th century, the Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens developed a mathematical model of mirages that is still used today.
What Causes Mirages
Mirages are a fascinating optical phenomenon that can occur on hot days. They are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. Mirages can take many forms, from shimmering pools of water to distant mountains that appear to be floating in the sky.
- Refraction: The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
- Density: The mass of a substance per unit volume.
- Temperature: The measure of the warmth or coldness of a substance.
- Pressure: The force exerted by a fluid on a surface.
- Humidity: The amount of water vapor in the air.
- Wind: The movement of air.
- Surface conditions: The nature of the surface over which the light is passing.
- Observer's perspective: The position of the observer relative to the mirage.
All of these factors can affect the formation and appearance of mirages. For example, mirages are more likely to occur on hot days because the difference in temperature between the ground and the air is greater. This difference in temperature causes the air near the ground to be less dense than the air higher up, which bends the light waves as they pass through it.
Mirages can be a beautiful and fascinating sight, but they can also be dangerous. Drivers who see a mirage of water on the road may be tempted to drive into it, which could lead to a crash. Mirages can also cause ships to sail off course and planes to crash.Refraction
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. This bending is caused by the difference in the speed of light in the two media. When light travels from a medium in which it is traveling slowly to a medium in which it is traveling faster, the light bends towards the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface of the second medium). Conversely, when light travels from a medium in which it is traveling quickly to a medium in which it is traveling slowly, the light bends away from the normal.
- Mirage
Mirages are a common example of refraction. Mirages occur when light passes through layers of air of different densities. The different densities of air cause the light to bend, creating the illusion of water on the horizon.
- Lenses
Lenses are another example of refraction. Lenses are made of a material that causes light to bend. This bending of light can be used to focus light, which is useful in a variety of applications, such as eyeglasses, telescopes, and cameras.
- Prisms
Prisms are also an example of refraction. Prisms are made of a material that causes light to bend. This bending of light can be used to separate light into different colors, which is useful in a variety of applications, such as rainbows and spectrometers.
- Optical fibers
Optical fibers are also an example of refraction. Optical fibers are made of a material that causes light to bend. This bending of light allows light to be transmitted over long distances without losing much of its intensity.
Refraction is a fundamental property of light. It is responsible for a wide variety of optical phenomena, including mirages, lenses, prisms, and optical fibers.
Density
Density is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume of a substance. It is an important property of matter because it affects many of its physical and chemical properties, including its behavior in response to light. In the context of mirages, density plays a crucial role in determining how light bends as it passes through different layers of air.
- Role in mirage formation
Mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. The greater the difference in density between two layers of air, the more the light will bend. This is why mirages are often seen on hot days, when the air near the ground is much hotter and less dense than the air higher up.
- Examples
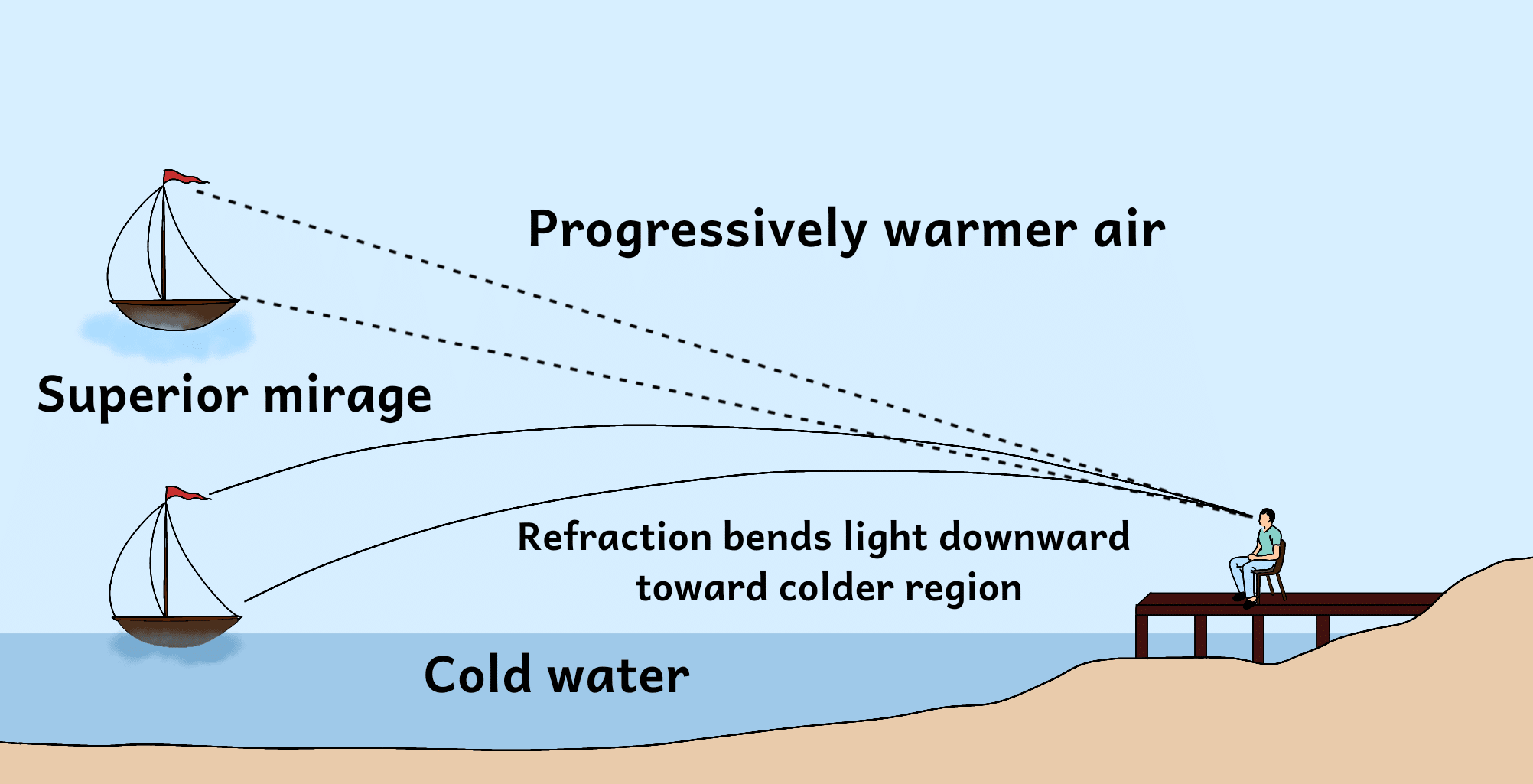
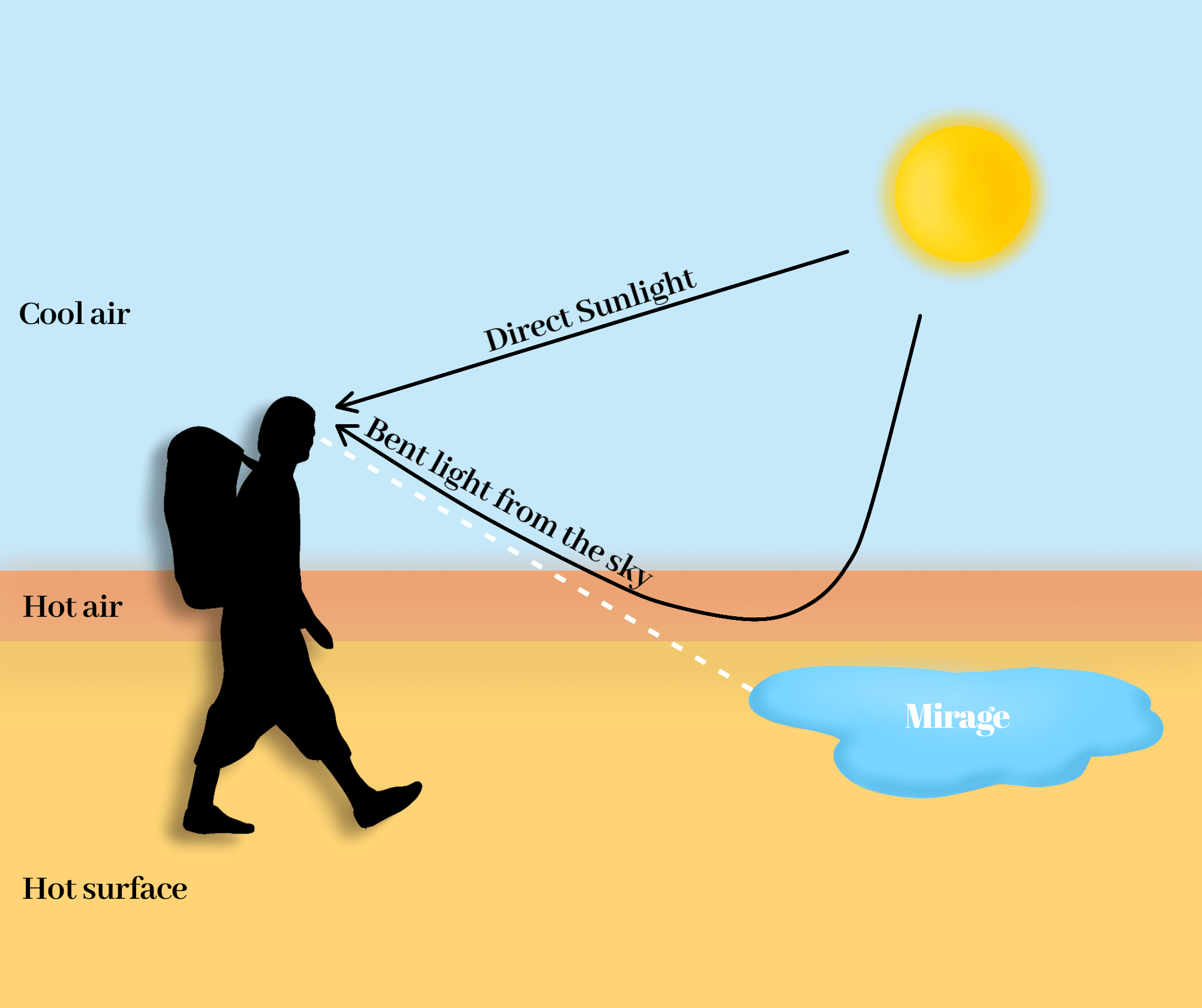
One common type of mirage is the inferior mirage, which appears as a pool of water on the horizon. This type of mirage is caused by the bending of light as it passes through a layer of hot air near the ground. The light is bent upwards, creating the illusion of water on the horizon.
- Implications
The density of air can also affect the appearance of mirages. For example, mirages are more likely to occur in dry climates, where the air is less dense. This is because the difference in density between the hot air near the ground and the cooler air higher up is greater in dry climates.
In conclusion, density is a key factor in the formation of mirages. The greater the difference in density between two layers of air, the more the light will bend, and the more likely a mirage is to occur.
Temperature
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. It is an important property of matter because it affects many of its physical and chemical properties, including its behavior in response to light. In the context of mirages, temperature plays a crucial role in determining how light bends as it passes through different layers of air.
- Role in mirage formation
Mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. The greater the difference in density between two layers of air, the more the light will bend. Temperature is one of the factors that affects the density of air. Warm air is less dense than cool air, so the difference in temperature between two layers of air can create a difference in density that is large enough to cause light to bend.
- Examples
One common type of mirage is the inferior mirage, which appears as a pool of water on the horizon. This type of mirage is caused by the bending of light as it passes through a layer of hot air near the ground. The light is bent upwards, creating the illusion of water on the horizon.
- Implications
The temperature of the air can also affect the appearance of mirages. For example, mirages are more likely to occur on hot days, when the air near the ground is much hotter and less dense than the air higher up. This is because the difference in temperature between the two layers of air is greater on hot days, which causes the light to bend more.
In conclusion, temperature is a key factor in the formation of mirages. The greater the difference in temperature between two layers of air, the more the light will bend, and the more likely a mirage is to occur.
Pressure
Pressure is the force exerted by a fluid on a surface. It is an important property of fluids because it affects many of their physical and chemical properties, including their behavior in response to light. In the context of mirages, pressure plays a crucial role in determining how light bends as it passes through different layers of air.
The pressure of a fluid is caused by the weight of the fluid above the point of measurement. The greater the depth of the fluid, the greater the pressure. This is why the pressure of the air at sea level is greater than the pressure of the air at the top of a mountain. The pressure of a fluid also increases with temperature. This is because the particles in a fluid move faster at higher temperatures, which increases the number of collisions between the particles and the surface of the fluid.
The pressure of the air can affect the formation of mirages. For example, mirages are more likely to occur on days when the air is calm and the pressure is high. This is because the calm air allows the layers of air to form more easily, and the high pressure helps to keep the layers of air in place.
Humidity
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. It is an important property of the atmosphere because it affects many weather phenomena, including the formation of clouds, fog, and rain. Humidity can also affect the formation of mirages.
- Role in mirage formation
Mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. The density of air is affected by its temperature and humidity. Warm air is less dense than cool air, and humid air is less dense than dry air. This means that when light passes from a layer of warm, humid air to a layer of cool, dry air, it will bend towards the normal.
- Examples
One common type of mirage is the inferior mirage, which appears as a pool of water on the horizon. This type of mirage is caused by the bending of light as it passes through a layer of hot, humid air near the ground. The light is bent upwards, creating the illusion of water on the horizon.
- Implications
The humidity of the air can also affect the appearance of mirages. For example, mirages are more likely to occur on humid days, when the air near the ground is more humid than the air higher up. This is because the difference in humidity between the two layers of air is greater on humid days, which causes the light to bend more.
In conclusion, humidity is a key factor in the formation of mirages. The greater the difference in humidity between two layers of air, the more the light will bend, and the more likely a mirage is to occur.
Wind
Wind is the movement of air. It is caused by differences in air pressure, which in turn are caused by differences in temperature. Wind can be strong or weak, and it can come from any direction. Wind plays an important role in the formation of mirages.
- Wind shear
Wind shear is the change in wind speed and direction over a short distance. Wind shear can cause mirages by bending light as it passes through layers of air with different wind speeds and directions.
- Turbulence
Turbulence is the random movement of air. Turbulence can cause mirages by disrupting the flow of light as it passes through the air.
- Updraft
Updrafts are currents of rising air. Updrafts can cause mirages by bending light as it passes through layers of air with different temperatures.
- Downdraft
Downdrafts are currents of sinking air. Downdrafts can cause mirages by bending light as it passes through layers of air with different temperatures.
Wind is a complex phenomenon that can have a significant impact on the formation of mirages. By understanding the role that wind plays, we can better understand the causes of mirages and how they can be predicted.
Surface conditions
The nature of the surface over which light is passing can have a significant impact on the formation of mirages. This is because the surface conditions can affect the way that light is reflected, refracted, and absorbed.
- Reflectivity
Reflectivity is the ability of a surface to reflect light. Highly reflective surfaces, such as mirrors, can cause mirages by reflecting light in such a way that it appears to come from a different direction. This can create the illusion of objects that are not actually there.
- Refractivity
Refractivity is the ability of a surface to bend light. This can cause mirages by bending light in such a way that it appears to come from a different direction. This can create the illusion of objects that are not actually there, or it can distort the appearance of objects that are actually there.
- Absorption
Absorption is the ability of a surface to absorb light. This can cause mirages by absorbing some of the light that is passing through it. This can create the illusion of objects that are not actually there, or it can make objects that are actually there appear to be darker.
Surface conditions can play a significant role in the formation of mirages. By understanding the way that light interacts with different surfaces, we can better understand the causes of mirages and how they can be predicted.
Observer's perspective
The position of the observer relative to the mirage can have a significant impact on its appearance. This is because the mirage is caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air with different densities. The observer's position determines which layers of air the light passes through, and this can affect the way that the mirage is seen.
- Distance from the mirage
The distance between the observer and the mirage can affect its appearance. Mirages that are close to the observer will appear to be more distorted than mirages that are further away. This is because the light from a close mirage has to pass through more layers of air to reach the observer, and this gives the air more time to bend the light.
- Height of the observer
The height of the observer can also affect the appearance of a mirage. Observers who are higher up will be able to see mirages that are further away than observers who are closer to the ground. This is because the light from a distant mirage has to pass through less air to reach an observer who is higher up.
- Angle of the observer's view
The angle at which the observer is looking at the mirage can also affect its appearance. Observers who are looking directly at a mirage will see it as a distorted image of the object that is causing the mirage. Observers who are looking at the mirage from an angle will see it as a more elongated image.
The position of the observer is an important factor to consider when trying to understand the causes of mirages. By understanding how the observer's position affects the appearance of a mirage, we can better understand the physics of mirages and how they are formed.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Causes of Mirages
Mirages are fascinating optical illusions that can occur on hot days. They are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. Mirages can take many forms, from shimmering pools of water to distant mountains that appear to be floating in the sky.
Question 1: What causes mirages?Mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. This bending of light is called refraction. When light passes from a medium in which it is traveling slowly to a medium in which it is traveling faster, the light bends towards the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface of the second medium). Conversely, when light passes from a medium in which it is traveling quickly to a medium in which it is traveling slowly, the light bends away from the normal.
Question 2: Why do mirages occur on hot days?Mirages are more likely to occur on hot days because the difference in temperature between the ground and the air is greater. This difference in temperature causes the air near the ground to be less dense than the air higher up. When light passes from the hot air near the ground to the cooler air higher up, it bends towards the normal. This bending of light can create the illusion of water on the horizon or other objects that are not actually there.
Question 3: What are the different types of mirages?There are many different types of mirages, but the most common are:
- Inferior mirage: This is the most common type of mirage, and it appears as a pool of water on the horizon. Inferior mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through a layer of hot air near the ground.
- Superior mirage: This type of mirage appears as an object that is floating in the sky. Superior mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through a layer of cold air near the ground.
- Fata morgana: This is a complex type of mirage that can create the illusion of elaborate scenes, such as castles or cities. Fata morgana mirages are caused by the bending of light as it passes through multiple layers of air of different densities.
Yes, mirages can be dangerous. Drivers who see a mirage of water on the road may be tempted to drive into it, which could lead to a crash. Mirages can also cause ships to sail off course and planes to crash.
Question 5: How can mirages be prevented?Mirages cannot be prevented, but they can be avoided. If you see a mirage, do not drive into it or sail your ship towards it. Instead, slow down and proceed with caution.
Question 6: What causes the shimmering effect that is often seen above hot surfaces?The shimmering effect that is often seen above hot surfaces is caused by the rising of hot air. Hot air is less dense than cool air, so it rises. As the hot air rises, it causes the air above it to become turbulent. This turbulence causes the light passing through the air to be scattered in all directions, which creates the shimmering effect.
Tips on Understanding the Causes of Mirages
Mirages are fascinating optical illusions that can occur on hot days. They are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. Mirages can take many forms, from shimmering pools of water to distant mountains that appear to be floating in the sky.
Tip 1: Understand the role of temperature.
Temperature is one of the most important factors in the formation of mirages. Hot air is less dense than cool air, so when light passes from a layer of hot air to a layer of cool air, it bends towards the normal. This bending of light can create the illusion of water on the horizon or other objects that are not actually there.
Tip 2: Consider the effects of humidity.
Humidity is another important factor in the formation of mirages. Humid air is less dense than dry air, so when light passes from a layer of humid air to a layer of dry air, it bends towards the normal. This bending of light can contribute to the formation of mirages, especially on hot and humid days.
Tip 3: Be aware of the impact of wind.
Wind can also affect the formation of mirages. Wind can create turbulence in the air, which can cause light to bend in unpredictable ways. This can lead to the formation of distorted or moving mirages.
Tip 4: Observe the surface conditions.
The nature of the surface over which light is passing can also affect the formation of mirages. For example, mirages are more likely to occur over flat surfaces, such as roads or deserts, because there is less turbulence in the air near the ground. Mirages are also more likely to occur over surfaces that are heated by the sun, such as asphalt or sand.
Tip 5: Pay attention to your perspective.
The position of the observer relative to the mirage can also affect its appearance. For example, mirages that are close to the observer will appear to be more distorted than mirages that are further away. The height of the observer can also affect the appearance of a mirage, as observers who are higher up will be able to see mirages that are further away.
Summary:
By understanding the causes of mirages, we can better understand how they are formed and how they can be predicted. This knowledge can help us to avoid the dangers that mirages can pose, such as driving into a mirage of water on the road.
Conclusion
Mirages are fascinating optical illusions that are caused by the bending of light as it passes through layers of air of different densities. Mirages can take many forms, from shimmering pools of water to distant mountains that appear to be floating in the sky.
The causes of mirages are complex, but they can be understood by considering the following factors:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Wind
- Surface conditions
- Observer's perspective
By understanding the causes of mirages, we can better understand how they are formed and how they can be predicted. This knowledge can help us to avoid the dangers that mirages can pose, such as driving into a mirage of water on the road.
Mirages are a reminder of the power of light and the beauty of the natural world. They are a testament to the fact that there is always more to learn about the world around us.
Unveiling Hector: The Unsung Hero Of The Fast And Furious Saga
Discover Neel Master: The Ultimate Image Editing Revelation For Creative Geniuses
Unveil The Apostolic Calling Of Henry B. Eyring: A Journey Of Faith And Leadership
What Causes Mirages?A Deep Dive into Optical Illusions Smore Science

The science behind…the highway mirage Imprint
What Causes Mirages?A Deep Dive into Optical Illusions Smore Science
ncG1vNJzZmieopqzpq%2FHZ5imq2NjsaqzyK2YpaeTmq6vv8%2Bamp6rXpi8rnvWoZitZZOWwrSx0makoqqRnLK0esetpKU%3D